Space telescopes are powerful instruments designed to capture images and data from objects in space. They operate beyond the Earth’s atmosphere, enabling them to capture high-resolution images that are unobtainable by ground-based telescopes. This article will explore the history, advantages, functionality, amazing discoveries, current and future space telescopes, and challenges of using space telescopes.
History of Space Telescopes
The First Space Telescope
The first space telescope, the Orbiting Astronomical Observatory (OAO-2), was launched in 1968 by NASA. The OAO-2 was designed to observe ultraviolet radiation and cosmic rays that are blocked by the Earth’s atmosphere. This event marked the beginning of a new era in astronomy, leading to the development of more advanced space telescopes.
The Evolution of Space Telescopes
Since the launch of the OAO-2, several other space telescopes have been developed and launched, each with advanced capabilities. Some of the most notable space telescopes include the Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-ray Observatory, the Spitzer Space Telescope, the Kepler Space Telescope, and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope.
The Advantages of Space Telescopes
No Atmospheric Interference
Space telescopes are able to capture high-quality images without atmospheric interference. The Earth’s atmosphere can cause distortion and blurring of images, making it difficult for ground-based telescopes to capture clear images.
High Resolution
Space telescopes have the ability to capture high-resolution images, enabling astronomers to see details that would otherwise be impossible to observe. This has led to numerous discoveries, including the detection of exoplanets and the discovery of new galaxies.
Large Field of View
Space telescopes have a wider field of view than ground-based telescopes, enabling astronomers to observe larger areas of the sky. This has led to the discovery of new stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects.
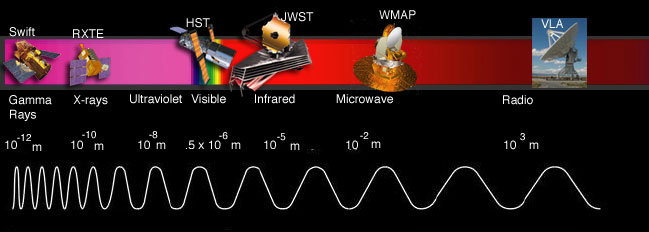
How Space Telescopes Work
Space telescopes operate using different systems depending on the wavelength of light they are designed to capture. The following are some of the systems used in space telescopes:
Optical Systems
Optical systems are designed to capture visible light, similar to how a traditional telescope operates. They use mirrors and lenses to focus light onto a detector, where it is then recorded.
Infrared Systems
Infrared systems are designed to capture infrared light, which is emitted by objects that are too cool to emit visible light. These systems use detectors that are sensitive to infrared light and can detect heat radiation.
Ultraviolet Systems
Ultraviolet systems are designed to capture ultraviolet light, which is absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere. These systems use detectors that are sensitive to ultraviolet light and can detect emissions from stars and other celestial objects.
X-ray Systems
X-ray systems are designed to capture X-rays, which are emitted by high-energy sources such as black holes and neutron stars. These systems use mirrors that are specially designed to reflect X-rays onto a detector, where it is then recorded.
Gamma-ray Systems
Gamma-ray systems are designed to capture gamma rays, which are emitted by high-energy sources such as supernovae and black holes. These systems use detectors that are sensitive to gamma rays and can detect emissions from these sources.
Amazing Discoveries Made by Space Telescopes
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope has made numerous groundbreaking discoveries, including the detection of dark matter, the discovery of exoplanets, and the observation of the most distant galaxy ever seen. Its high-resolution images have provided astronomers with unprecedented views of the universe.
Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory was launched by NASA in 1999 and is designed to capture X-rays emitted by high-energy sources in the universe. It has made significant discoveries, including the detection of a black hole that is 12 billion times more massive than the sun, and the discovery of a pulsar that is spinning at a rate of 716 times per second.
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope was launched in 2003 and is designed to capture infrared light emitted by objects in space. It has made significant discoveries, including the detection of an exoplanet with the same size as Jupiter but with a temperature that is twice as hot as most stars.
Kepler Space Telescope
The Kepler Space Telescope was launched in 2009 and is designed to detect exoplanets by monitoring changes in the brightness of stars. It has discovered thousands of exoplanets, including Earth-sized planets that are in the habitable zones of their stars.
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope is the upcoming space telescope set to be launched by NASA in 2021. It is designed to capture images and data from the universe in infrared light, providing astronomers with new insights into the universe’s origins, the formation of galaxies, and the possibility of life beyond our solar system.

Challenges of Using Space Telescopes
Space telescopes come with their challenges, including:
Cost
Building and launching a space telescope is an expensive undertaking, requiring billions of dollars in funding.
Maintenance
Space telescopes are in remote locations, making it challenging to perform repairs and maintenance.
Limited Lifetime
Space telescopes have a limited lifetime, usually around 10 to 20 years. After this time, they become obsolete, and new space telescopes need to be launched to replace them.
Conclusion
Space telescopes have revolutionized our understanding of the universe, providing us with unprecedented views of objects and phenomena that were once beyond our reach. The Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-ray Observatory, the Spitzer Space Telescope, the Kepler Space Telescope, and the upcoming James Webb Space Telescope have made significant contributions to astronomy, and new space telescopes are being developed to further our understanding of the universe.
FAQs
- How do space telescopes differ from ground-based telescopes? Space telescopes operate beyond the Earth’s atmosphere, allowing them to capture high-quality images without atmospheric interference. They also have a wider field of view and can capture high-resolution images that ground-based telescopes cannot.
- What kind of discoveries have been made by space telescopes? Space telescopes have made numerous groundbreaking discoveries, including the detection of exoplanets, the observation of distant galaxies, and the detection of black holes and other high-energy sources.
- What are the challenges of using space telescopes? Space telescopes are expensive to build and launch, and their maintenance is challenging. They also have a limited lifetime, usually around 10 to 20 years.
- How do space telescopes capture different wavelengths of light? Space telescopes use different systems to capture different wavelengths of light, including optical systems, infrared systems, ultraviolet systems, X-ray systems, and gamma-ray systems.
- What is the upcoming space telescope set to be launched by NASA? The James Webb Space Telescope is the upcoming space telescope set to be launched by NASA in 2021. It is designed to capture images and data from the universe in infrared light, providing astronomers with new insights into the universe’s origins, the formation of galaxies, and the possibility of life beyond our solar system.








No Comment! Be the first one.